The global fresh produce market, encompassing fruits and vegetables in their natural or minimally processed form, is expanding rapidly as consumer preferences shift toward healthier, sustainable food options. In 2024, the market was valued at USD 270.51 billion and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4% to reach USD 451.37 billion by 2034.
Fresh produce remains a staple in global diets and is increasingly viewed as essential in addressing rising lifestyle-related health concerns. The market’s transformation is being fueled by innovations in supply chains, packaging, and digital commerce, alongside growing demand for organic, locally sourced, and sustainably grown produce.
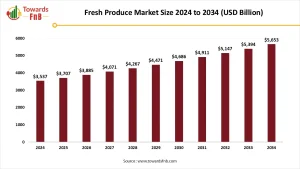
Market Overview
Fresh produce fruits and vegetables that are sold fresh (not frozen or canned) is vital to the global food supply chain. These foods are a major source of vitamins, fiber, antioxidants, and essential nutrients, making them indispensable for human health. As global consumers become more health-conscious and environmentally aware, fresh produce consumption is gaining momentum in both developed and emerging economies. Moreover, rising urbanization, improvements in cold-chain infrastructure, and innovations in packaging and retail distribution are enabling producers and retailers to deliver higher-quality produce with longer shelf lives.
Get a Sample Now: https://www.towardsfnb.com/download-sample/5477
Market Dynamics
Drivers
- Health & Wellness Trends
- Rising awareness about nutrition and immunity has increased consumption of natural, whole foods like fruits and vegetables.
- Fresh produce is seen as preventive medicine in the fight against obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
- Organic & Clean Label Movement
- Increased demand for non-GMO, organic, and chemical-free food has significantly boosted premium fresh produce sales.
- Consumers are willing to pay more for traceability and transparency.
- Urbanization and Lifestyle Shifts
- Busy urban lifestyles are fueling demand for pre-cut, ready-to-cook produce formats, including packaged salads and veggie snack packs.
- Advancements in Cold Chain and Packaging
- Improved logistics and packaging technologies have enhanced shelf life, reduced spoilage, and enabled global trade in fresh produce.
- E-commerce Expansion
- Online grocery platforms and mobile apps are making fresh produce more accessible, especially in urban and semi-urban areas.
Restraints
- High Perishability
- Fresh produce has a short shelf life, requiring efficient logistics and rapid distribution to prevent wastage and maintain quality.
- Price Volatility
- Seasonal availability, climate variability, and supply chain disruptions can lead to fluctuating prices and inconsistent supply.
- Limited Infrastructure in Emerging Markets
- Lack of cold storage facilities, poor road connectivity, and inefficient handling methods in developing nations hinder market expansion.
- Regulatory Barriers
- Stricter safety and import/export regulations in various countries can delay or limit cross-border trade in fresh produce.
Opportunities
- Growth in Plant-Based & Vegan Lifestyles
- Increasing adoption of plant-based diets is pushing up demand for a diverse range of fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Smart Agriculture & Vertical Farming
- Innovations such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and vertical farming are enabling year-round cultivation with reduced environmental impact.
- Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Channels
- Subscription boxes, community-supported agriculture (CSA), and farm-to-home delivery platforms are emerging as profitable, scalable business models.
- Emerging Markets
- Expanding middle-class populations in Asia, Africa, and Latin America present untapped growth potential for both domestic production and imports.
Challenges
- Food Waste
- Nearly one-third of fresh produce is lost or wasted due to poor storage, transit damage, and overstocking, affecting profitability and sustainability.
- Climatic Risks & Natural Disasters
- Droughts, floods, and temperature extremes directly impact yield, quality, and availability of fresh produce globally.
- Intense Market Competition
- The commoditized nature of fresh produce makes it challenging for brands to differentiate and build customer loyalty without added services or quality marks.
- Supply Chain Disruptions
- Global events such as pandemics or geopolitical instability can cause severe disruptions in sourcing, pricing, and availability.
Market Growth Drivers
- Rising Health Awareness
With growing concerns about obesity, heart disease, and lifestyle-related illnesses, consumers are gravitating toward whole, nutrient-rich foods. Fresh produce is increasingly seen as a daily necessity, especially among millennials and Gen Z.
- Urbanization and Changing Lifestyles
The shift toward urban living has driven demand for convenient, ready-to-eat produce. Pre-washed salads, fruit snacks, and cut vegetables are now common in urban retail spaces and food service outlets.
- Demand for Organic and Locally Sourced Produce
Consumers prefer produce that is free from pesticides and GMOs. Local farming, farm-to-table concepts, and organic certification are becoming key differentiators in product choice.
- Expansion of Modern Retail and E-commerce
Hypermarkets, supermarkets, and online grocery platforms have widened the reach of fresh produce. Technology enables better inventory management, freshness tracking, and customized delivery.
- Growth of Cold Chain Logistics
Advancements in temperature-controlled storage and transportation have minimized food spoilage and waste, facilitating the global trade of fresh produce with higher quality standards.
Market Opportunities
- Innovative Packaging and Shelf-Life Technologies
Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), biodegradable materials, and intelligent labels are revolutionizing the way fresh produce is stored and sold, offering opportunities to improve product safety and shelf life.
- Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Delivery Models
The rise of health-focused delivery services and subscription boxes presents new avenues for fresh produce sales, especially in urban centers and tech-savvy populations.
- Vertical Farming and Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)
Urban farming, hydroponics, and vertical farming solutions are gaining traction as sustainable, local alternatives to traditional agriculture, ensuring year-round availability of high-quality produce.
- Emerging Markets
Rising middle-class populations in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are driving demand for higher-quality, packaged, and imported produce, creating new growth frontiers.
Grab the Databook and Discover Key Industry Insights Instantly: https://www.towardsfnb.com/download-databook/5477
Top Companies in the Fresh Produce Market
The fresh produce market is highly competitive and features a mix of multinational corporations and regional players focused on innovation, sustainability, and supply chain efficiency. Key strategies among these companies include product diversification, strategic partnerships, sustainable farming practices, and advancements in packaging and distribution. The following are some of the prominent companies operating in the global fresh produce market:
- Del Monte
- Dole plc
- Greenyard
- NatureSweet Tomatoes
- Cargill, Incorporated
- Hain Celestial
- Dole Food Company, Inc.
- Dairy Farmers of America, Inc.
- General Mills Inc.
- Danone
- United Natural Foods, Inc.
- GCMMF (Gujarat Cooperative Milk Marketing Federation Ltd.)
- Organic Valley
- Conagra Brands, Inc.
- Eden Foods
- SunOpta
- Pacific Fresh Produce, Inc.
- Taylor Farms
Get detailed pricing and reports now : https://www.towardsfnb.com/price/5495
Segmentation Analysis
By Type
- Fruits
Apples, bananas, citrus fruits, berries, melons, grapes, etc. - Vegetables
Leafy greens, root vegetables, tomatoes, onions, bell peppers, broccoli, etc. - Organic Produce
Certified organic fruits and vegetables grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers. - Conventional Produce
Widely available, non-organic fruits and vegetables grown with standard agricultural methods.
By Distribution Channel
- Supermarkets/Hypermarkets
Offer variety, quality assurance, and modern packaging options. - Traditional Grocers & Wet Markets
Still dominant in many developing countries due to affordability and local sourcing. - Online Retail/E-Commerce
A rapidly growing channel driven by digital convenience, particularly in urban areas. - Specialty Stores & Organic Markets
Cater to premium and health-conscious consumers looking for organic, pesticide-free, or locally sourced products. - Foodservice & Institutional Buyers
Hotels, restaurants, hospitals, and schools sourcing bulk quantities of high-quality produce.
Regional Analysis
North America
- Market Share (2024): ~28%
- U.S. and Canada dominate with high per capita produce consumption. Organic produce and convenience-focused formats are in high demand. Farm-to-table, traceability, and clean labeling drive consumer choices.
Europe
- Market Share (2024): ~25%
- Countries like Germany, the UK, and France lead the market. High regulatory standards, strong demand for organic and local produce, and sustainable agriculture initiatives support steady growth.
Asia-Pacific
- Fastest-growing region, projected CAGR >6.5%
- Driven by urbanization, income growth, and improved logistics in China, India, Japan, and Southeast Asia. Increasing government support for horticulture and smart agriculture boosts supply chain efficiency.
Latin America
- Export-driven region
- Key exporters of tropical and off-season fruits. Brazil, Mexico, Chile, and Peru are major producers. Domestic markets are also growing due to rising middle-class health awareness.
Middle East & Africa (MEA)
- Emerging but promising
- Imports dominate in many GCC countries due to arid climates. Innovations like hydroponics and vertical farming are gaining ground. South Africa and Egypt serve as major regional suppliers.
Outlook and Future Opportunities
The fresh produce market is set to grow significantly over the next decade, driven by a confluence of health consciousness, urbanization, retail modernization, and supply chain innovations. While fruits and vegetables have always been dietary essentials, their role in preventive health, clean eating, and sustainability is making them central to the future of food.
Stakeholders from growers and processors to retailers and tech platforms must focus on quality assurance, sustainability, innovation, and accessibility to capture long-term value in this dynamic market.
